Approach
- Expose the patient as for breast examination
- Inspect
- Note asymmetry of the chest wall
- Prosthesis can be identified by the presence of surgical scars and by a different shape from the normal breast contour
- Flap reconstruction
TRAM flap
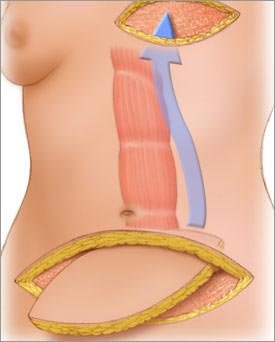
Latissimus dorsi flap

DIEP free flap - Implant reconstruction: rounder, lie of breast usually higher; Becker implant may have a palpable subcutaneous filling port in the axilla

- Palpate
- Percuss
- Auscultate
Types of Breast Reconstruction
- Subcutaneous prosthesis
- Submuscular implant
- Tissue expander
- Myocutaneous flap
- TRAM - transverse rectus abdominis
- LD - latissimus dorsi
- DIEP - deep inferior epigastric artery pedicle graft
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Implant |
|
|
| Myocutaneous flaps |
|
|