Pathology
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Derived from capillary endothelial cells or from fibrous tissue
- Linked to human herpes virus 8 (HHV8) aka Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus KSHV
- Classical Kaposi sarcoma
- First described in Askenazi Jews
- Found on legs of elderly men
- Confined to skin
- Not fatal
- AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma
- Found in 1/3 patients with AIDS (diagnostic of AIDS)
- More common in homosexual patients
- 1/3 develop a second malignancy (eg leukaemia, lymphoma)
- Endemic (central African)
- Aggressive invasive tumour
- Ultimately fatal
- Good response to chemotherapy
- Transplantation associated Kaposi sarcoma
- Following high-dose immunosuppressive therapy
- Often regress when treatment stopped
Approach
- Examine as for any lump
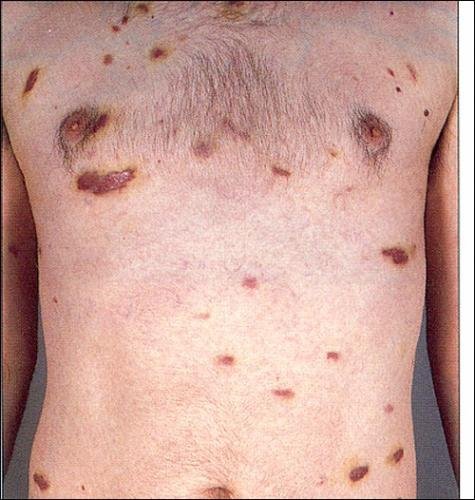
- Inspect
- Purple papules or plaques
- Solitary or multiple
- Can be found anywhere on skin or on mucose of any organ but usually found on the limbs, mouth, tip or nose or palate
Completion
- Take history
- Ethnic origin (Jew, black)
- Previous transplant
- Underlying immunosuppression (without saying HIV or AIDS directly)
Treatment
- Leave alone if asymptomatic and if patient does not want intervention
- Intervene only when extensive or for cosmetic reasons
- Local radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy - INFa, doxorubicin, intralesional vinblastine
- (if in context of HIV infection - adequate anti-retroviral therapy)