Cardiac Assessment
- Non-invasive
- Pulse
- Blood pressure
- ECG
- Echocardiography: systolic function, cardiac filling, valve function, general morphology
- Indicators of cardiac index: Consciousness, CRT, urine output
- Invasive
- ABGs
- Serum lactate: rising levels indicate poor cardiac index
- Gastric tonometry - adequacy of splanchnic perfusion is estimated from gastric intramucosal pH using gastric probe. ("belief" that gut is first oran system to reflect poor peripheral perfusion)
- Mixed venous sats - SvO2 shows oxygen extraction
- Arterial line
- CVP monitoring - absolute with response to fluid challenges
- Pulmonary artery catheterisation
- TOE: more detailed picture of left heart + thoracic aorta
- Indicators if cardiac index:
Cardiac Output
Heart rate x Stroke volume
Determinants of Stroke volume:
| Preload: | Contractility | Afterload: |
|
Degree of stretch of cardiac myocytes in diastole
|
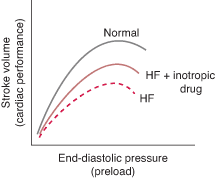
Determined by Frank-Starling curve
Increased by
|
Ventricular wall tension
|
|
Hypovolaemia
|
Stunning, infarction Hypoxia Acidosis Tachyarrythmias |
Pharmacological support
- Inotropic drugs
- Adrenergic agonists: Adrenaline, noradrenaline
- Dopaminergic agonists (with some adrenergic activity): Dopamine, dobutamine, dopexamine
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Milrinone, enoximone - inhibits degradation of intracellular cAMP; causes increase in intracellular concentration of calcium ions leading to enhanced contractility
- Calcium chloride
- Vasoconstrictors
- Vasodilators
| Drug | Alpha-1 | Beta-1 | Beta-2 | DA1 | Notes |
| Vasoconstriction | HR+ FOC+ |
Bronchodilation | Increased splanchnic / renal blood flow | ||
| Adrenaline |
+++ | +++ | ++ | ||
| Noradrenaline |
+++ | + | Vasopressor | ||
| Dopamine |
+ | + | + | +++ | Dose dependent effects No evidence of renoprotective benefit |
| Dobutamine |
+++ | ++ | Inodilator Useful in low output/high resistance |
||
| Salbutamol | + | +++ | Acute severe asthma |
Problems with inotropes
- Arrhythmias
- Increased myocardial oxygen consumption and demand
Electrical support
- Cardiac pacemaker (chronotropic support)
Mechanical support
- Intra-aortic balloon pump (for myocardium capable of recovery): - reduces afterload "sucking" effect on deflation, increases coronary blood flow
- Inserted percutaneously/direct vision into femoral artery.
- Passed until tip lies distal to arch vessel
- Balloon triggered by ECG to deflate during systole (reduces arterload) and inflate during diastole (displaces blood to coronary arteries retrogradely)
Complications: femoral artery damage, ischaemia, haemolysis
- Ventricular assist device