Flow of Cerebrospinal fluid
Blood brain barrier
- Histological / physiological barrier
- Formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells + astrocyte foot processes
- Substances able to pass: Lipids / lipid permeables (opiates, GAs, respiratory gases, glucose)
- Disrupted by: infections, tumours, trauma, iscahemia
Areas outside BBB: Hypothalamus, posterior pituitary
Cerebral blood flow
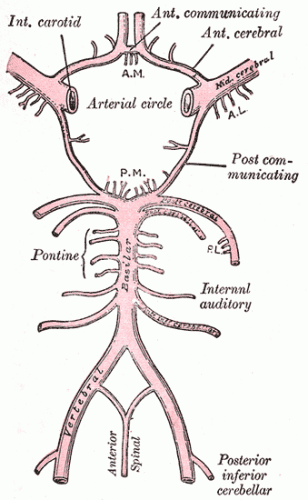
- 500ml / kg // ~750ml/min (15% cardiac output)
- Autoregulated between 50-150mmHg
- Myogenic response: rise in pressure in artery causes reflex contraction increasing vascular resistance, keeping flow constant
- Vasodilator "washout": locally produced vasodilators washed out leading to vascular resistance
- CO2: hypercarbia increases blood flow (by vasodilation)
- Hypoxia: produces vasodilation (less pronouced)
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure = Mean Arterial Pressure - Intracranial pressure
Must be >70mmHg to maintain adequate brain perfusion
Cushing Reflex
- Elevated ICP
- Leads to hypertension
- Reflex bradycardia
Monroe-Kellie Doctrine
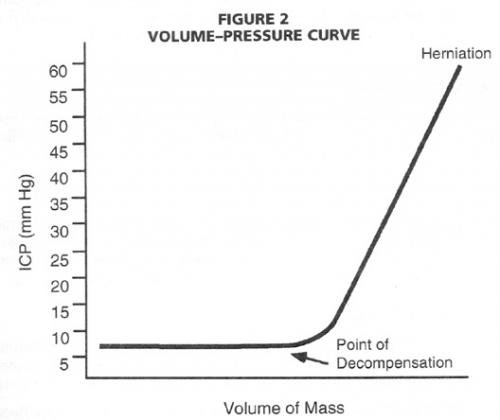
- Cranial cavity considered to be rigid sphere with non-compressible contents
- Increased ICP - of once compartment means shift in others
- Brain: Tumours, cerebral oedema, BIH
- blood: ICB - subdural, extradural, SAH, intracerebral
- CSF: hydrocephalus
Signs of raised ICP
- Headache, nausea, vomiting
- LOC
- Papilloedema
- Brain herniation: leading to herniation, coma, respiratory failure, death
- Subfalcine: cingulate gyrus herniates beneath falx
- Foramen magnum: displacement of medulla and cerebellar tonsils
- Transtentorial: Uncus of temporal lobes passes through tenttorial hiatus
[Attachment of falx / tentorium]
Management of Head Injury
- Determine GCS
- Imaging
- Indications: persisting neurology, persisting headache/vomiting; reduced level of consciousness
- Suspected penetrating injury
- Suspected base of skull injury
- Consider transfer to neurosurgical centre
- Monitoring
- CVP
- Arterial pressure
- Intracranial pressure monitoring
- Support:
- Temperature regulation
- Careful fluid balance
- Management of Raised intracranial pressure - 3Ps
Brain
- Sedation / antiepileptics / barbiturates
- Mannitol - reduce brain oedema
- Fluid restriction
- ??Steroids
Blood - SBP
- Gelofusin / fluid bolusing - maintain MAP
- Inotropic support
- PCO2 control - ventilator settings
- Evacuate haematoma
CSF
- VP Shunt
- External ventricular drainage
- Improve venous drainage - remove obstructions around neck, nurse upright, reduce ventilatory PEEP